The divide between Astronomy and Astrology
Astronomy and Astrology developed at around the same time, like two sides of the same coin. Yet one is a pristine field of science, while the other is considered more like a religious practice.
What is the difference between ‘Astronomy’ and ‘Astrology’ and why is it that the latter is considered as Pseudo-science? And does being born when the Sun/Moon were aligned with a specific pattern of stars, really make someone have a short temper? Let’s start from their origins.
Imagine, you are standing in an open field, with no watches or cell phones. How would you tell what time it is? It seems natural to look at the sky, and look at the sun and go “hmm, must be around evening”. We can tell and keep track of time at least vaguely, by looking at the sun during the day, but what about, at night? One could argue, we can look at the moon. That can work, but the moon’s path in the night sky is not as simple and as periodic as the Sun’s and requires more elaborate calculations. Also, what if it’s a New Moon that night?
Ok, the chances of you being stranded in a field like that, without even a cell phone are minimal in today’s world. But it was the reality for people in the 40th century BC, around the time of the dawn of early Human Civilizations
1. The oldest human civilization that we currently know of is the Sumerian civilization, said to have settled in the regions of southern Mesopotamia at around 4000 BC.
2. The Babylonians were their successors and the Babylonian civilization flourished in the 18th century BC, with their city capital in Babylon, now in modern-day Iraq.
3. Small settlements were formed near the river Nile by Egyptian farmers around 5000 BC which evolved into the Egyptian civilization by 3100 BC, famous for its great achievements in arts, architecture, and medicine.
4. Around the same time as the Sumerians, Farmer settlements were formed around the Indus River which is considered, the birthplace of the Indian Civilization. The major and the most advanced, Indus valley cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro flourished in the 26th Century BC.
One of the many important factors for any civilization to prosper is to be able to keep track of time. To know what’s the right time to sow seeds, to go hunting or fishing. When to harvest, when to hoard food supplies in case of a drought, especially for cities that relied on rivers. Keeping a record of river patterns, high and low tides was essential for sustenance.
Well then, how did early human civilizations keep track of time back then?
They looked to the sky, at the stars! They always seem to stay in that same pattern(relatively). In fact, using stars is so much more efficient, that one can even predict what month of the year it is by confirming the presence of specific patterns of stars in the night sky, which we named ‘Constellations’ or ‘asterisms’ (Patterns smaller than constellations).
Keeping track of and recording time is as old as civilization itself. Primitive methods of timekeeping have existed since the Neolithic period. Humans used external factors and repeating patterns that they saw in nature to keep track of time. The position of the rising and the setting sun and the phases of the Moon, to track days and weeks, months and years.
The Sumerians are credited with having the first complete calendar based on the cycles of the moon. Their calendar consisted of 12 Months. The ancient Indian calendar too was based on the phases of the moon and had 12 months. The Egyptian calendar was based on the Sun and had 365 days in a year.
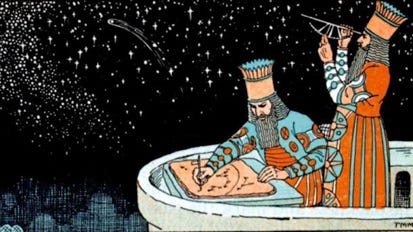
The Babylonians followed the 12-month calendar too and created the concept of the 12 zodiac signs that we know today. On the vast canvas of the sky, the Sun seems to periodically pass through these 12-star patterns in one year, in a specific order. By knowing this order, tides, floods, and droughts can be predicted, because a specific pattern of stars would be present in the night sky, at those times.
Early Stargazers realized that some of the “not so stationary stars” in the night sky are actually planets! and they too seem to follow a periodic path through the night sky. This is what we call Astronomy. The study of Celestial Objects. The Stars, the Sun, the Moon, and the Planets. As Astronomy developed, People started associating these planets with seasons and kept a record of them showing up in the sky to help them perform many religious rituals.

There was a major divide in beliefs when people started associating those constellations and planets not as indicators, but as the “reasons” behind the change in seasons, floods and droughts, and any other natural phenomena. People started looking at the planets and stars as “Gods” and celestial beings, who can control the weather and even aspects of their lives. The people born under a specific constellation were given a label of that Zodiac as their “sun sign/moon sign” and people started making claims about their personalities and even about their futures!
Predicting the weather, using the position of stars and the phases of the moon is one thing, but making claims about an individual depending on which star pattern they were born under, is something totally different. This is what led to what we know today as Astrology.
We know now, that the tides on Earth are caused by the motion of the Moon, and yes, according to Physics, anything with mass attracts anything else with mass in the universe, but they need to be pretty close to each other, or their masses massive or comparable enough, to have any notable effects. A planet like Jupiter, though substantially huge, won’t really have any effect on someone walking on Earth. To believe that it does even theoretically is just absurd.

The night sky filled with stars without any light pollution would have looked absolutely breathtaking to the early astronomers. A line by Willem Dafoe’s character in the movie ‘Platoon’ describes the night sky beautifully,
I love this place at night, the stars, there’s no right or wrong in them, they’re just there
That’s what astronomers believe; the stars don’t really affect any happenings here on Earth. They are just there.
Early civilizations looked to the stars, trying to understand them and use them to predict the time and find directions. They used the periodicity of the planets and the phases of the moon to give themselves a sense of the flow of time and order. Early Astronomy was created out of the curiosity of humans when they looked at the night sky. The urge to make sense of the randomly distributed star patterns and Nature’s unpredictability.
But somewhere along the way, Astrology got separated from Astronomy. While Astronomy is now regarded as one of the most pristine sciences, Astrology is considered a pseudo-science due to the lack of any hard evidence. Many cultures around the world still see Astrology in high regard but most of its popularity is limited only to some religions and Believers.
Image credits:
Sumerian settlements: Source. Babylonian civilization: A 16th-century depiction of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon (by Martin Heemskerck). Settlements in Egyptian civilization: Source. Indus valley civilization: An artist's impression of what life may have been like in the Indus valley.




Excellent👌
Such a beautiful well written article ☺️